ESG Explained: A Simple Guide for Businesses in 2026
Introduction: Why ESG Matters More Than Ever
ESG is everywhere — in boardrooms, investment decisions, regulations, and customer expectations. But for many businesses, ESG still feels vague, complex, or overwhelming.
So what does ESG actually mean, and why is it becoming unavoidable?
In this guide, we break down Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) in plain English, explain why it matters in 2025, and show how companies can approach ESG in a practical, value-driven way.
What Does ESG Stand For?
ESG stands for:
E – Environmental
S – Social
G – Governance
Together, these three pillars are used to evaluate how responsibly a company operates, beyond just financial performance.
ESG helps investors, regulators, partners and customers understand:
How a company impacts the environment 🌍
How it treats people 🤝
How it is managed and governed 🏛️
Environmental (E): How Your Business Impacts the Planet
The Environmental pillar focuses on how a company interacts with the natural world.
Key environmental ESG factors include:
Carbon emissions and climate impact
Energy efficiency and renewable energy use
Biodiversity and land use
Water consumption
Waste management and recycling
Deforestation and ecosystem protection
In 2025, environmental performance is no longer optional. With climate risk, biodiversity loss, and stricter reporting requirements, businesses are expected to measure, reduce, and disclose their environmental footprint.
🌱 This is where nature-based solutions, reforestation, and ecosystem restoration — core to CloudForests’ mission — play a critical role in credible environmental ESG strategies.
Social (S): People, Communities and Society
The Social pillar examines how a company treats its employees, customers, suppliers and wider community.
Common social ESG topics:
Employee wellbeing, safety and fair pay
Diversity, equity and inclusion (DEI)
Human rights and ethical supply chains
Community engagement and social impact
Customer trust, data privacy and product responsibility
Strong social ESG performance builds:
Higher employee retention
Stronger brand trust
More resilient supply chains
Companies that ignore social factors face reputational damage, talent shortages, and operational risk.
Governance (G): How the Company Is Run
Governance refers to leadership, transparency, and accountability at the top of an organisation.
Governance ESG factors include:
Board structure and diversity
Executive compensation
Ethical decision-making
Anti-corruption policies
Risk management and compliance
Shareholder rights and transparency
Good governance ensures that environmental and social commitments are real, measurable, and enforced — not just marketing claims.
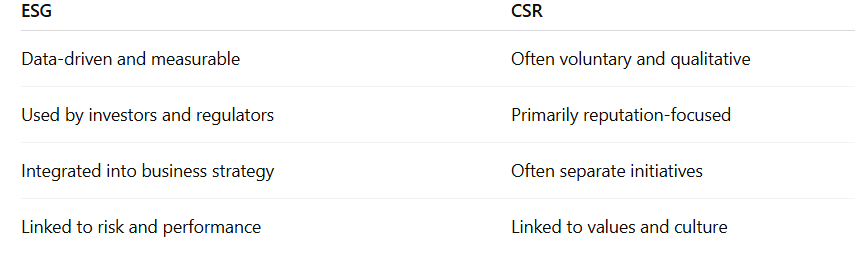
ESG vs CSR: What’s the Difference?
Many people confuse ESG with CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility).
In short:
CSR is about intention. ESG is about evidence.
Why ESG Is So Important in 2026
ESG is being driven by three major forces:
1. Regulation
New rules like the EU CSRD require companies to report ESG data with the same rigour as financials.
2. Investors
Investors increasingly assess ESG performance to:
Reduce risk
Identify long-term value
Meet their own regulatory obligations
3. Customers & Talent
Consumers and employees want to support businesses that:
Protect nature
Act ethically
Contribute positively to society
Ignoring ESG now creates financial, legal, and reputational risk.
How Businesses Can Start with ESG (Without the Headache)
You don’t need to do everything at once. A practical ESG starting point includes:
Understand your biggest impacts
Environmental, social and governance risks vary by industry.Measure what matters
Focus on meaningful, material metrics — not vanity numbers.Use credible environmental actions
Nature-based solutions, biodiversity protection, and verified climate projects strengthen ESG credibility.Be transparent
Honest reporting beats exaggerated claims. Avoid greenwashing — and greenhushing.Build ESG into strategy
ESG works best when it supports long-term business resilience.
ESG and the Role of Nature-Based Solutions
High-quality ESG strategies increasingly rely on real environmental outcomes, not just offsets or pledges.
Protecting forests, restoring ecosystems, and supporting biodiversity:
Reduces climate risk
Strengthens environmental ESG scores
Aligns with global sustainability frameworks
Creates measurable, long-term impact
🌳 This is why platforms like CloudForests exist — to connect businesses with transparent, nature-positive ESG solutions.
Final Thoughts: ESG Is About Long-Term Value
ESG is not a trend or a box-ticking exercise. It’s a framework for building resilient, responsible, future-proof businesses.
Companies that embrace ESG:
Manage risk better
Attract capital more easily
Build trust with customers and employees
Contribute to a healthier planet and society
And in 2026, that’s not just good ethics — it’s good business.